Surprisingly, it is estimated that today only 39% of network problems are detected by operators, while 61% of faults are first discovered by end-users, with many going unreported. Although some disruptions are caused by accidents or natural disasters and are unavoidable, the majority of faults can be avoided, making imperative the implementation of a robust, cost-effective and holistic quality assurance method to continuously guarantee the best customer experience.
With 5G, the scenario for quality of experience has reached unprecedented complexity as networks must support multiple devices (for home, health, and enterprise; mobiles, IoT), protocols, dynamic configurations, data, new and legacy technologies, in a multi-vendor, cloud-native, Multi-Access Edge Compute-enabled, virtualized, automated and sliced ecosystem. In addition, network design, deployment and operations are driven by 5G’s expected outcomes, such as low latency, low energy, high and scalable bandwidth, massive M2M IoT, configurable private slices for dedicated QoS, retainable connectivity across landscapes, high-speed download and upload, and high throughput.
Addressing service assurance with a holistic perspective requires strategies that combine passive and network element data with active test data. Passive monitoring offers critical deep customer insights that enrich Customer Experience Management (CEM) by using root cause analysis (RCA) of big data, currently slow and hard to process. Additionally, with 5G's increasing dynamism and complexity, user plane passive monitoring has become too expensive and unsustainable to manage. Alternatively, active testing methods use synthetic traffic with near real-time customer experience test agent data to enable fast, simple, lightweight, easy to automate and cost-effective drill down root cause analysis. Consequently, a combinational approach is recommended for a 360° quality assurance for voice, data, video, social networking, messaging, and emergency services. Another challenge with user plane traffic is the 80% plus is encrypted so analysis methods are required that can interpret the customer activity whilst maintaining encryption.
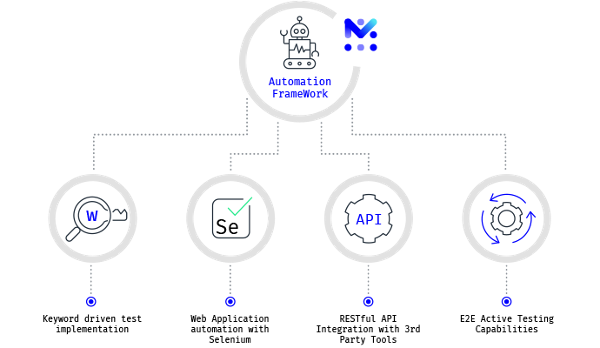
Over and above, an efficient service assurance approach must support not only DevOps methodologies, which allow improved communication, collaboration, and integration among development and operations teams, but also continuous integration/continuous delivery/continuous testing (CI/CD/CT) processes, which entail the rapid and reliable release of updates and new deployments. RESTful API makes possible the addition of an automated testing component and the compatibility with third-party systems which are crucial to interrelate DevOps and CI/CD/CT pipelines. Together they deliver improved quality and streamline operational efficiency, by permanently monitoring the service lifecycle, validating them at all stages from network design to technology integration, deployment, operation, and maintenance. In the 5G environment with minimized bottlenecks, operators can deploy new services and functions constantly and flawlessly into the network in increasingly shorter roll-out cycles.
Having the above in mind, service assurance starts already in the lab phase, long before deployment. Lab testing is crucial to ensure a fault-free launch and includes functional testing, load testing, application performance testing under load, network function interoperability segmentation, regression testing, slice SLA testing, and isolation testing. It comprises measuring and foreseeing call performance and capacity, validating system scalability with various subscriber loads and traffic simulation and service level emulation end-to-end in a controlled manner, identifying performance ceilings and bottlenecks, verifying new mobility features and standards, planning capacity, ratifying message content, and facilitating unattended test modes for users by emulating real-world scenarios with heavy load and long duration stability tests.
At the pinnacle of true 360° service assurance is automation overarching the network ecosystem with systematic and uninterrupted actions that ensure QoS, and implicitly QoE. In addition, automation covers analytics, active segmented diagnosis, and PCAP analysis to further strengthen RCA or degradation detection and help trim down service assurance capex and opex to manageable levels. In the same way, automated active end-to-end testing with synthetic traffic analysis using real user devices aligned with passive monitoring provides a correlation of key service indicators (KPIs) across RAN, CORE, IMS and BSS systems to ensure comprehensive quality of experience for voice, data, video, social networking, messaging and emergency services. Automation also encompasses virtual testing to validate core network, IMS, billing, charging, policy, and security functions. Moreover, it allows both control plane and user plane interfaces to continually measure QoE, and the generation of actionable insights from cross-correlation analyses across the network, the user, the applications, and the service KPIs, in both domestic and international markets. Additionally, an enriched, periodic, scheduled, and automated service assurance empowers quality teams to aggregate signaling KPIs and metrics from various sources, benchmark against the competition, and view alerts of potential wider and local issues that are below SLAs in the Core and RAN respectively.
In a nutshell, an integrated service assurance solution means treating the network from a holistic perspective instead of compartmentalizing it. Implementing systemic, looped, and automated testing from lab to live to operations, enables operators to perform upgrades and rollouts in a timely, cost-effective, and reliable manner, ensure the quality and performance of their services and networks, prevent and detect failures before impact, and, consequently, reduce the average 61% of faults first detected by users.






Give us your comments
Let us know what you thought about this article